An Updated Overview of Protein Tags
An Updated Overview of Protein Tags
A guide to recent and growing trends in protein tags
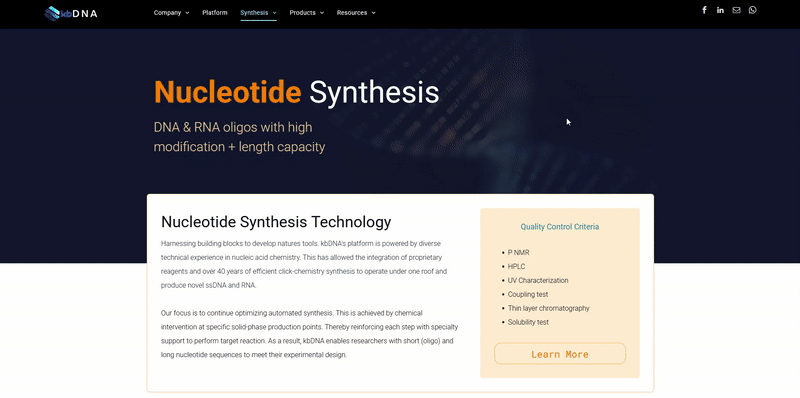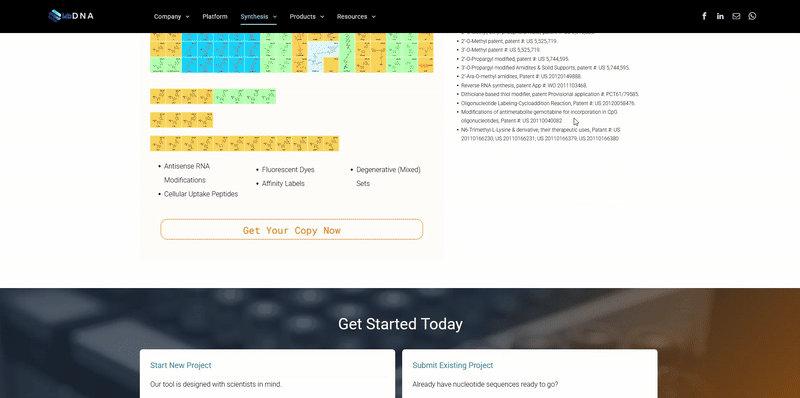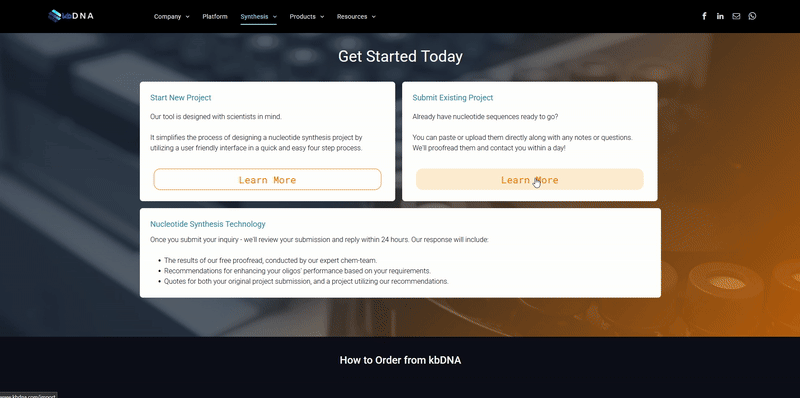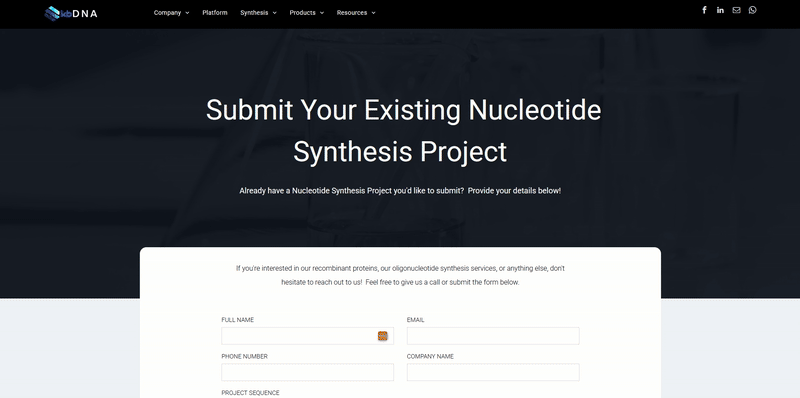
Introduction
Protein tagging has been around for decades, but their traditional uses are not frequent enough to make them common lab knowledge. Recent improvements in biochemical techniques have been increasing their frequency as creative design and analysis tools. In this overview, we offer a guide for the variety of different protein tags that are trending in recent growth.
This guide will cover:
- Principle Affinity Tags
- Biotin Tags
- Epitope Tags
- Fluorescent Tags
Principle Affinity Tags
Arg-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Immobilize functional proteins on flat surface |
| Application | Studying interactions with ligands |
| Feature | GFP with Arg-tag can be bound to mica surfaces |
| Application | Scanning probe microscopy applications |
| Terminus Attachment | C-term |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial |
| Measured Biochemistry | |
|---|---|
| Purity | 95% |
| Yield | 44% |
His-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Immobilization, linear recognition motif |
| Application | Purification (most common method) |
| Feature | Strongest interaction with immobilized metal ion matrice |
| Application | Immobilized metal-affinity chromatography (IMAC) |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Viral |
| Measured Biochemistry | |
|---|---|
| Purity | 95% |
| Yield | 44% |
GST
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Increased solubility, highly antigenic |
| Application | Purification |
| Feature | Amplified detection |
| Application | Protein expression |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
Biotin Tags
Strep-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Matrix regenerable, recognition motif |
| Application | Purification and detection |
| Feature | Eukaryotic cell surface display, surface immobilization |
| Application | SPR CHIPS, NMR, Crystallization, Protein interactions |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Insects; Plants; Synthetic |
Streptavadin-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Increase proteolytic stability, high affinity immobilization |
| Application | Detection and Expression support |
| Feature | Newer low affinity versions |
| Application | Purification |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Insects; Plants; Synthetic |
Epitope Tags
c-myc-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | 9E10 immunological recognition |
| Application | Immunoblotting/WB, Immunoprecipitation, Flow Cytometry |
| Feature | Convertible Reagent |
| Application | Protein engineering |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Insects |
FLAG-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Peptide bound to antibody (M1) |
| Application | Purification |
| Feature | Consistent non-denaturing conditions |
| Application | Purifying active fusion proteins |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian |
| Measured Biochemistry | |
|---|---|
| Purity | 90% |
HA-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Viral antibody recognition |
| Application | Detection |
| Feature | Anti-HA antibodies specific |
| Application | Expression |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Mammalian |
| Measured Biochemistry | |
|---|---|
| Yield | Low |
Fluorescent Tags
Luciferase
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Luminescent dye |
| Application | Detection |
| Feature | Serve as a reporter immediately upon translation |
| Application | In-situ hybridization, RNA processing, RNA transfection |
| Terminus Attachment | N-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Insects |
GFP
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Intrinsic fluorescence can permit native detection |
| Application | Detection |
| Feature | No antibody needed for detection |
| Application | Monitor gene expression, protein folding, and targeting |
| Terminus Attachment | N-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian; Insects |
S-tag
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Specific linear recognition motif |
| Application | Detection |
| Feature | RNase S specificity |
| Application | Diverse assays; quantitative, colorimetric no antibody |
| Terminus Attachment | N or C-terminal |
| Compatible Domain | Bacterial; Yeast; Mammalian |
Points to Consider
- FLAG mAb purification systems have not always been stable and often require expert intervention.
- The presence of C-terminal tags can potentially contribute to a protein's loss of function. Particularly in the case of enzymes.
- Streptavadin-binding peptide (SBP) is only attachable to the C-terminus
- S-tag in low pH elution may alter protein properties and limit the matrix reproducibility
- anti-myc antibody antibody purification is inconsistent and has been proven to result in poor yields
References
- Nilsson et al. (1997a)
- Lazzaroni et al. (1985)
- Goldstein et al. (1992)
- Crespo et al. (1997)
- Makrides (1996)
- McLean et al. (2001)
- Nilsson et al. (1997b)
- Wang et al. (1996)
- Podbielski et al. (1992)
- Jones et al. (1995)
- Morandi et al. (1984)
- Kaldalu et al. (2000)
- Jones et al. (1995)
- Rubinfeld et al. (1991)
- Smith (2000)
- Gerdes and Kaether (1996)
- Los et al. (2008)
- Terpe (2003)
- Imagawa et al. (1982)
- Fritze and Anderson (2000)
- Tai et al. (1988)
- Kuliopulos and Walsh (1994)
- Kwatra et al. (1995)
- Tai et al. (1988)
- Karp and Oker-Blom (1999)
- Kolodziej and Young (1991)
- Terpe (2003)
- Kimple and Sondek (2002)
- Stevens (2000)
- Bornhorst and Falke (2000)
- Stevens (2000)
- Abdulaev et al. (2005), Biao et al. (2004), Ruan et al. (2004)
- Fritze and Anderson (2000)
- Berlot (1999)
- Nilsson et al. (1997b)
- Skerra and Schmidt (2000)
- Sano et al. (1998)
- Terpe (2003)
- Stevens (2000)
- Li (2011)
- Terpe (2003)
- Nelson et al. (1999)